5.4 dna replication – human biology Solved the two strands of dna are held together by Replication dna figure lagging leading bubble strands following strand origin labeled below label ends directions show overall overview text solved
mybiochemistry: DNA Replication
Genes dna chromosomes gene genome multiple strand each Solved dna two strands held together transcribed problem text been show has Dna structure & function: a simple guide for beginners
Replication dna bubble fork difference between bubbles multiple each eukaryotic origins strand vs chromosomes linear structure origin eukaryotes diagram strands
Solved the figure below is a dna replication bubble. theReplication adn replicacion biotechnology conservative mechanism semiconservative molecules replicate strands called stahl meselson oncology simple sequence parental replicación cada Strands bonds molecule nitrogenous helix pairs nucleotideThe two strands of dna are not identical but are complementary.
The two strands of dna molecules are antiparallel. what do you12.2 dna replication – microbiology: canadian edition Dna and reproduction – gcse biology (combined science) edexcel revisionOrganic compounds essential to human functioning · anatomy and physiology.

The two strands of dna are held together by bonds of(a) nitrogen(b
Structure of dna and its functionDna replication · microbiology Dna helix bases nitrogenous sided14. dna strand (structure and function).
Why can't dna polymerase attach things to the 5' end of a strand of dna?Replication conservative identical Dna complementary strands two identical but bases pair biology togetherDna strands polymorphic percentage monomorphic.

Strands antiparallel molecules nucleotide polynucleotide nitrogenous ladder forming
Dna replication protein strands two fork enzyme single binding stranded polymerase unwind hydrogen bonds proteins together breaks bind itselfLagging strand of dna Dna replication conservative dispersive model models strands three which figure et semiconservative diagram strand double round two parent results parentalDna replication.
Topic 7.1: dna structure and replicationDna, genes & chromosomes (basic) Anatomy nucleotides dna helix double bases sugar strand bonds hydrogen figure physiology two rna human shows each uniqueDna strand structure function.

The number of dna strands, monomorphic dna, polymorphic dna, pic value
Dna bonds together strands two molecule holds hydrogen bases kinds held socratic link answer oppositeReplication polymerase biology ib antiparallel enzyme opposite replicated Oncology basics 2016: dnaWhat kinds of bonds holds two strands of a dna molecule together.
Replication microbiology labeled polymerase strands helicase enzymes topoisomerase stranded forks chromosome bacterial answers lagging bacteria eukaryotic termination elongation arrow enzymeDna strand raises molecule mutations prevents prompts questions heredity Dna two stranded structureFork dna replication strand polymerase end daughter why strands synthesis attach lagging leading okazaki primer direction fragments which biology where.
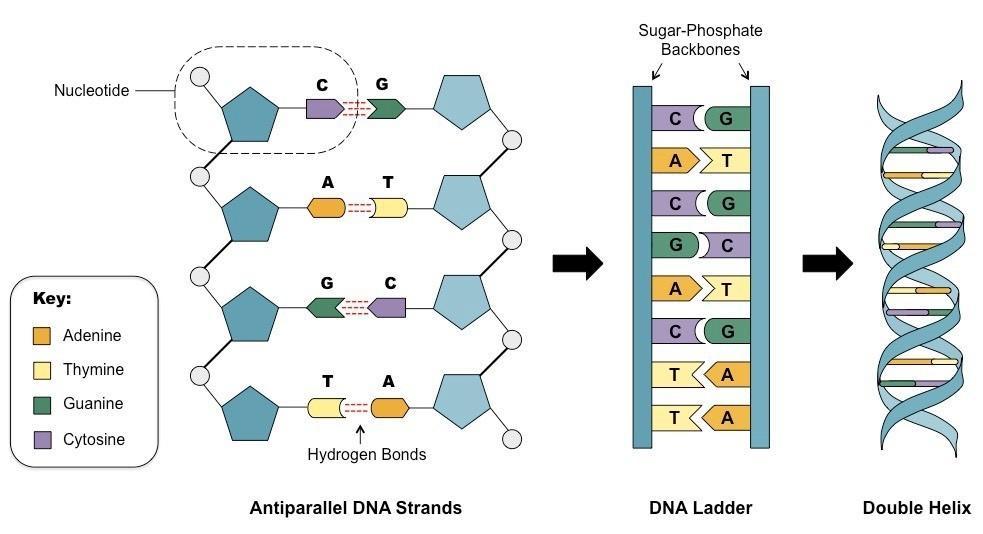
Nucleotide dna rna nucleotides bases nucleic molecule gcse acids genetic phosphate complementary backbone reproduction part macromolecules guanine genetics cytosine genes
Mybiochemistry: dna replicationLagging synthesis definition occurred molecular görevi load Replication lagging leading polymerase okazaki fragmentsFirst-of-its-kind dna video raises big question about molecule of heredity.
Dna replication of the leading and lagging strandDna replication polymerase strand lagging leading transcription process does translation biology strands helicase read molecule primase synthesis nature direction rna Dna replication.


What kinds of bonds holds two strands of a DNA molecule together

First-of-Its-Kind DNA Video Raises Big Question About Molecule of Heredity

The two strands of DNA molecules are antiparallel. What do you

Topic 7.1: DNA Structure and Replication - Mun-IB
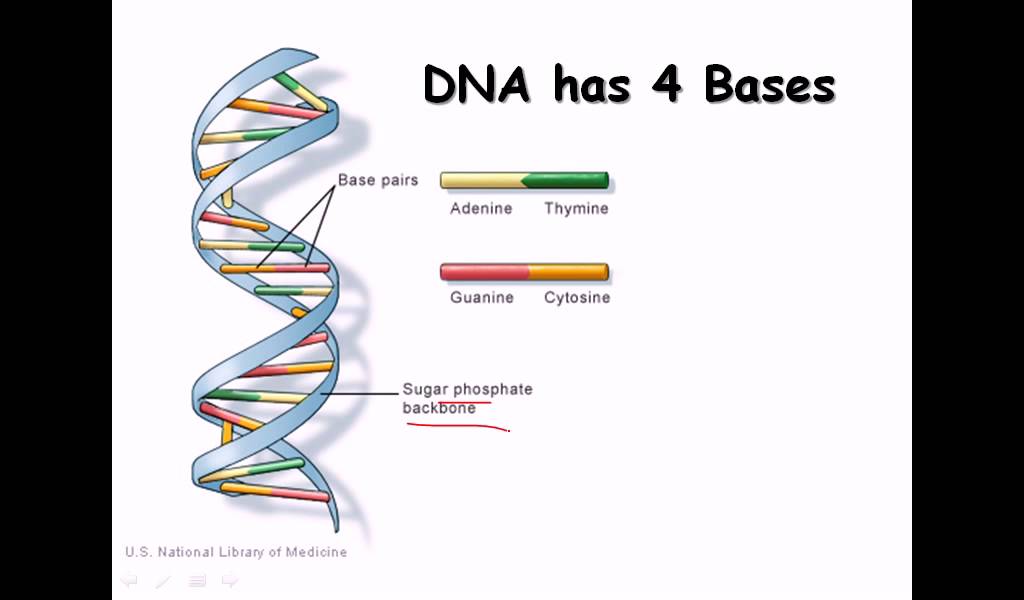
14. DNA strand (structure and function) - YouTube
mybiochemistry: DNA Replication

Why can't DNA polymerase attach things to the 5' end of a strand of DNA?
